Historic numbers of Americans live by themselves as they age
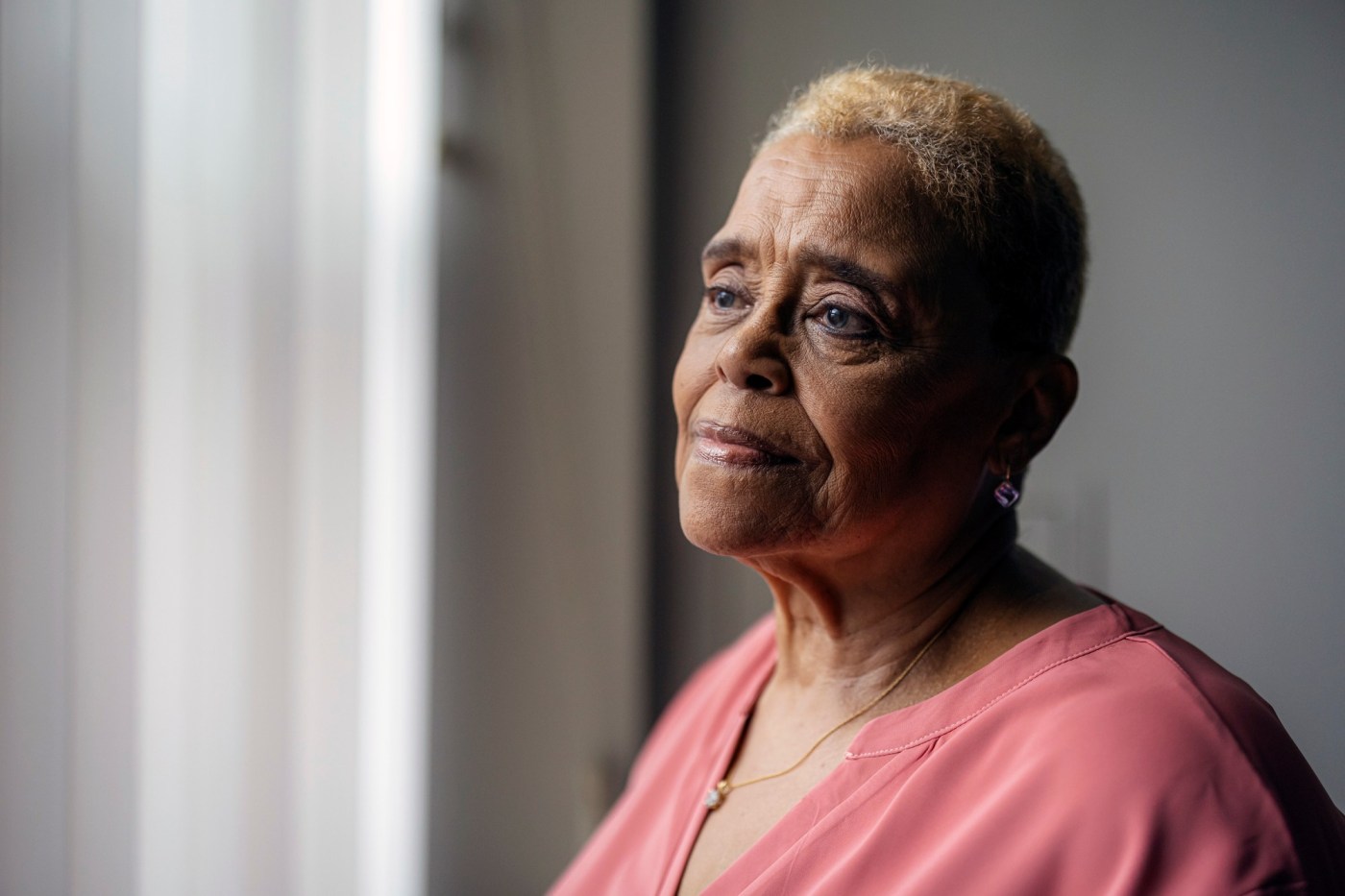
Gerri Norington, 78, never wanted to be on her own as she grew old.
But her first marriage ended in divorce, and her second husband died more than 30 years ago. When a five-year relationship came to a close in 2006, she found herself alone — a situation that has lasted since.
“I miss having a companion who I can talk to and ask ‘How was your day?’ or ‘What do you think of what’s going on in the world?’” said Norington, who lives in an apartment building for seniors on the South Side of Chicago. Although she has a loving daughter in the city, “I don’t want to be a burden to her,” she said.
Related Articles
Cyberattacks plague the health industry. Critics call feds’ response feeble and fractured
Opinion: If you were diagnosed with Alzheimer’s, would you want a choice?
Opinion: Proposition 35 harms the very communities it promises to help
Opinion: Prop. 35 will help ensure better health care for more Californians
Deadly high blood pressure during pregnancy is on the rise
Norington is part of a large but often overlooked group: the more than 16 million Americans living alone while growing old. Surprisingly little is known about their experiences.
This slice of the older population has significant health issues: Nearly 4 in 10 seniors living alone have vision or hearing loss, difficulty caring for themselves and living independently, problems with cognition, or other disabilities, according to a KFF analysis of 2022 census data.
If help at home isn’t available when needed — an altogether too common problem — being alone can magnify these difficulties and contribute to worsening health.
Studies find that seniors on their own are at higher risk of becoming isolated, depressed, and inactive, having accidents, and neglecting to care for themselves. As a result, they tend to be hospitalized more often and suffer earlier-than-expected deaths.
Getting medical services can be a problem, especially if older adults living alone reside in rural areas or don’t drive. Too often, experts observe, health care providers don’t ask about older adults’ living situations and are unaware of the challenges they face.
During the past six months, I’ve spoken to dozens of older adults who live alone either by choice or by circumstance — most commonly, a spouse’s death. Some have adult children or other close relatives who are involved in their lives; many don’t.
In lengthy conversations, these seniors expressed several common concerns: How did I end up alone at this time of life? Am I OK with that? Who can I call on for help? Who can make decisions on my behalf if I’m unable to? How long will I be able to take care of myself, and what will happen when I can’t?
This “gray revolution” in Americans’ living arrangements is fueled by longer life spans, rising rates of divorce and childlessness, smaller families, the geographic dispersion of family members, an emphasis on aging in place, and a preference for what Eric Klinenberg, a professor of sociology at New York University, calls “intimacy at a distance” — being close to family, but not too close.
The most reliable, up-to-date data about older adults who live alone comes from the U.S. Census Bureau. According to its 2023 Current Population Survey, about 28% of people 65 and older live by themselves, including slightly fewer than 6 million men and slightly more than 10 million women. (The figure doesn’t include seniors living in institutions, primarily assisted living and nursing homes.)
By contrast, 1 in 10 older Americans lived on their own in 1950.
This is, first and foremost, an older women’s issue, because women outlive men and because they’re less likely to remarry after being widowed or divorcing. Twenty-seven percent of women ages 65 to 74 live alone, compared with 21% of men. After age 75, an astonishing 43% of women live alone, compared with only 24% for men.
The majority — 80% — of people who live alone after age 65 are divorced or widowed, twice the rate of the general population, according to KFF’s analysis of 2022 census data. More than 20% have incomes below $13,590, the federal poverty line in 2022, while 27% make between that and $27,180, twice the poverty level.
Of course, their experiences vary considerably. How older adults living alone are faring depends on their financial status, their housing, their networks of friends and family members, and resources in the communities where they live.
Attitudes can make a difference. Many older adults relish being independent, while others feel abandoned. It’s common for loneliness to come and go, even among people who have caring friends and family members.
“I like being alone better than I like being in relationships,” said Janice Chavez of Denver, who said she’s in her 70s. “I don’t have to ask anybody for anything. If I want to sleep late, I sleep late. If I want to stay up and watch TV, I can. I do whatever I want to do. I love the independence and the freedom.”
Chavez is twice divorced and has been on her own since 1985. As a girl, she wanted to be married and have lots of kids, but “I picked jerks,” she said. She talks to her daughter, Tracy, every day, and is close to several neighbors. She lives in the home she grew up in, inherited from her mother in 1991. Her only sibling, a brother, died a dozen years ago.
In Chicago, Norington is wondering whether to stay in her senior building or move to the suburbs after her car was vandalized this year. “Since the pandemic, fear has almost paralyzed me from getting out as much as I would like,” she told me.
She’s a take-charge person who has been deeply involved in her community. In 2016, Norington started an organization for single Black seniors in Chicago that sponsored speed dating events and monthly socials for several years. She volunteered with a local medical center doing outreach to seniors and brought health and wellness classes to her building. She organized cruises for friends and acquaintances to the Caribbean and Hawaii in 2022 and 2023.
Now, every morning, Norington sends a spiritual text message to 40 people, who often respond with messages of their own. “It helps me to feel less alone, to feel a sense of inclusion,” she said.
In Maine, Ken Elliott, 77, a retired psychology professor, lives by himself in a house in Mount Vernon, a town of 1,700 people 20 miles northwest of the state capital. He never married and doesn’t have children. His only living relative is an 80-year-old brother in California.
Ken Elliott, a retired psychology professor, lives by himself in a house in Mount Vernon, Maine. His only living relative is a brother in California. Elliott is thinking about how to put together a team of people who can help him age in place. “Aging without a mythic family support system — which everyone assumes people have — is tough for everybody,” Elliott says. (Ken Elliott/KFF Health News/TNS)
For several years, Elliott has tried to raise the profile of solo agers among Maine policymakers and senior organizations. This began when Elliott started inquiring about resources available to older adults living by themselves, like him. How were they getting to doctor appointments? Who was helping when they came home from the hospital and needed assistance? What if they needed extra help in the home but couldn’t afford it?
To Elliott’s surprise, he found this group wasn’t on anyone’s radar, and he began advocating on solo agers’ behalf.
Now, Elliott is thinking about how to put together a team of people who can help him as he ages in place — and how to build a stronger sense of community. “Aging without a mythic family support system — which everyone assumes people have — is tough for everybody,” Elliott said.
In Manhattan, Lester Shane, 72, who never married or had children, lives by himself in an 11-by-14-foot studio apartment on the third floor of a building without an elevator. He didn’t make much money during a long career as an actor, a writer, and a theater director, and he’s not sure how he’ll make ends meet once he stops teaching at Pace University.
“There are days when I’m carrying my groceries up three flights of stairs when I think, ‘This is really hard,’” Shane told me. Although his health is pretty good, he knows that won’t last forever.
“I’m on all the lists for senior housing — all lottery situations. Most of the people I’ve talked to said you will probably die before your number comes up,” he said with mordant humor.
Then, Shane turned serious. “I’m old and getting older, and whatever problems I have now are only going to get worse,” he said. As is the case for many older adults who live alone, his friends are getting older and having difficulties of their own.
The prospect of having no one he knows well to turn to is alarming, Shane admitted: “Underneath that is fear.”
Kate Shulamit Fagan, 80, has lived on her own since 1979, after two divorces. “It was never my intention to live alone,” she told me in a lengthy phone conversation. “I expected that I would meet someone and start another relationship and somehow sail off into the rest of my life. It’s been exceedingly hard to give up that expectation.”
When I first spoke to Fagan, in mid-March, she was having difficulty in Philadelphia, where she’d moved two years earlier to be close to one of her sons. “I’ve been really lonely recently,” she told me, describing how difficult it was to adjust to a new life in a new place. Although her son was attentive, Fagan desperately missed the close circle of friends she’d left behind in St. Petersburg, Florida, where she’d lived and worked for 30 years.
Four and a half months later, when I called Fagan again, she’d returned to St. Petersburg and was renting a one-bedroom apartment in a senior building in the center of the city. She’d celebrated her birthday there with 10 close friends and was meeting people in her building. “I’m not completely settled, but I feel fabulous,” she told me.
What accounted for the change? “Here, I know if I want to go out or I need help, quite a few people would be there for me,” Fagan said. “The fear is gone.”
As I explore the lives of older adults living alone in the next several months, I’m eager to hear from people who are in this situation. If you’d like to share your stories, please send them to [email protected] .
KFF Health News is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues and is one of the core operating programs of KFF — the independent source for health policy research, polling and journalism.
©2024 KFF Health News. Distributed by Tribune Content Agency, LLC.